Eventual Consistency (Software Design)
An Eventual Consistency is a consistency model that guarantees the consistent state of data.
If all involved systems agree on the equal state of the data, that is, no updates are occurring, the data is considered to be eventual consistent.
Example
In the following example, Client A accesses System A for a write operation at (informal: an unspecific point in time, where and ).
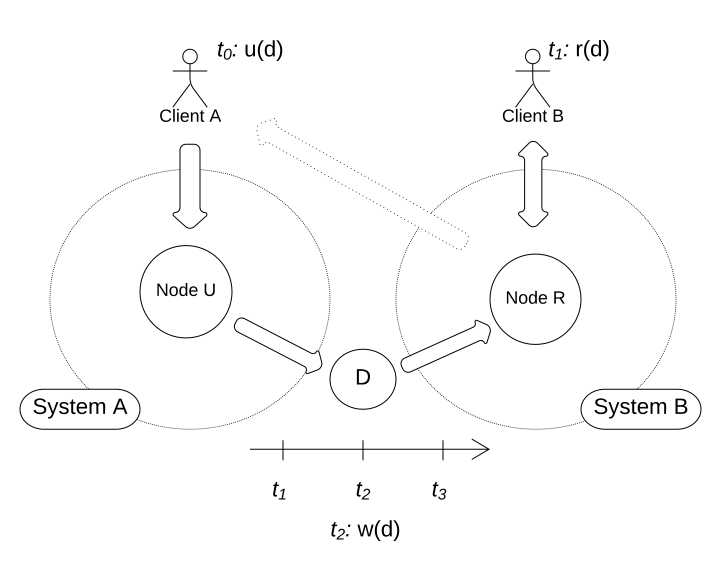
- At , Client B queries the data, which returns the data from from the set that was updated before .
- At , the data gets updated in .
- At , the system has reached eventual consistency.
Client B will now receive the data that is considered to be eventual consistent.
Likewise, Client A will not receive the updated data at (that is, requesting the update of the data, then immediately querying the update will respond with the old data from .)
Eventual Consistency is not reserved to systems where the boundaries are denoted through hardware-infrastructure. In a monolithic system, problems arise through caching: The monolithic system is considered to be Eventual Consistent when both the original data and it's cache are reconciled to the same state, i.e. if both contain the same data.
see also